We use cookies to enhance your experience. Read our policy so you can understand the types of cookies we use, the information we collect using cookies and how that information is used.Privacy Policy
Close
Confirm choices
The first using of Elastomeric Bearing (also named Rubber Pad or Block Bearing) in record can be traced back to the year of 1936, for a railway construction in suburban area of Paris, France.
Details
Laminated Elastomeric Bearing·
Using History
The first using of Elastomeric Bearing (also named Rubber Pad or Block Bearing) in record can be traced back to the year of 1936, for a railway construction in suburban area of Paris, France.
After WW II, the west countries began to extensively use this kind of bearings but not until 1958 the extensive and profound experiences were accumulated.
Today Elastomeric Bearings are commonly used for structural construction(steel or concrete) needs worldwide and has proven their durability and satisfactory performance.

Elastomeric bearings installed on piers
(Daguang elevated highway, IEC supplied 4000+ pcs of elastomeric bearings)
Design Principle
Elastomeric bearings function basically as an elastic and load-transferring connector between superstructure and substructure. Vertical loads from the structure itself and traffic loads, wind forces and centrifugal forces are absorbed and transmitted onto the substructure without restraints.
Vertical loads (from deck and traffic, etc) are taken and absorbed by the rubber in compression and horizontal deflections in shear (expansion and contraction).

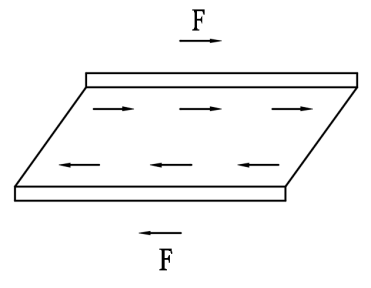
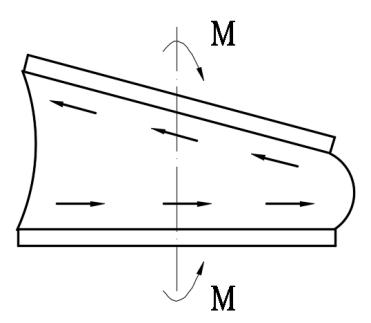
vertical load shear load rotation
The elastomeric block allows angular rotation and horizontal translation up to the design level through deformation thanks to the material characteristics of “Solid fluid” (the elastomer).
The horizontal reinforcement layers which are made of construction steel plates prevent the spreading of the elastomer under vertical loads whilst resist any arising tensile forces to the elastomer, thus high vertical stiffness (compressive stiffness) is achieved and yet the horizontal stiffness is maintained comparatively low;
The interleaving and vulcanization process, which chemically bonds the steel plates into the separated elastomer layers, provide shear and pressure resistant.
The reinforcing plates are encased in elastomer (a thin cover of rubber is arranged) and thus permanent protection against corrosion is obtained.

Intermediate reinforcing steel plate (often S255, stainless steel is also available upon request)
Location holes (fixing holes) inside the elastomer can be drilled to prevent slippage for purpose of installation when designed.

With holes
Applied standards
lEuropean Standard: EN 1337-3;
lBritish Standard: BS 5400-9.1, BS 5400-9.2;
lAmerican Standard: AASHTO M251-06(2011)Plain and Laminated Elastomeric for Bridge Bearings;
lAustralian Standard: AS5100 Part 4, Section 12.
IEC is underway of obtaining CE certification for Elastomeric Bearings as per EN standard and the certificate of Performance of Constancy was cycled till date for other types of bearings. We can also design and fabricate as per other standards and specifications.
Advantages of using Elastomeric Bearings compared with steel bearings
ØLow in cost and light in weight;
ØIf the permissible shear movement of the elastomeric bearing itself is not enough, which means a larger movement is required to be accommodated, then a sliding mechanism of stainless steel plates in combination with virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene(PTFE) sheet can be arranged. Otherwise, this additional sliding mechanism is not necessary and not so often as well;
ØSimple structure for design and fabrication;
ØLong service life (the elastomeric bearing have been proven to have a fairly long service life of 40 years);
ØConsiderable convenience in installation, maintenance, and even replacement, for some types even no any additional steel structure necessary in certain cases;
ØFor not sliding elastomeric bearings, actually free of maintenance when reliably installed;
ØCan be designed to act as dampers which help improve anti-seismic function for the structure(such as high-damping rubber bearing);
ØAble for visible inspections of structure and components;
Ø Comparatively more tolerance over installation errors;
Ø More readily compensate for minor construction irregularities.


Vulcanized PTFE, round/rectangular rubber bearings
Disadvantages of using Elastomeric Bearings compared with steel bearings
ØRequires larger space for installation under same request of vertical load;
ØNot as well suited for multi-rotation as pot bearings;
ØMay “slip” out of place with time if not properly fixed in place;
ØGenerates more vertical deflection than pot bearings;
ØExhibits varying extent of vertical deflection from bearing to bearing.
Application fields
ØEspecially suitable for small and medium loading, movement and rotation;
ØSmall permissible concrete pressure;
ØBuildings, viaducts, bridges, railways, piping, vessels, theaters, stadium or other structures;
ØCan be used as isolators for structures (LRB or HDRB, refer to Seismic Devices);
ØCan be used also as dampers in some conditions;
ØSuitable for temperature range from -30℃ to +50℃, up to 70 for short period.
Types of rubber choice
ØNeoprene Rubber (polychloroprene), CR in short; carries higher chemical resistance against environmental (particularly ultra-violet, oil and ozone) and weathering influences; more suitable for ageing resistance request;
ØNatural Rubber(polyisoprene), NR in short; carries higher mechanical and physical resistance due to its lower deformation resistance and larger damping effect; the processing of NR is also more environmentally friendly; more suitable for seismic, dynamical and cold regions;
ØCR/NR, means a core of NR and external shell of CR (usually several mm). This is probable an optimal combination of both benefits while maintaining a cost effective method.
Types based on outer shape of the bearing
ØRectangular types (including square);
ØCircular types;
In addition to above listed common used shapes where IEC Corporation has conventional moulds for fabrication during vulcanization process, the custom shapes like clipped corners, skewed, tapered or crown are also available by our design upon request. But customers shall note those uncommon shapes will cost premium due to mould modifications or new moulds.

Illustration of a tapered bearing
Tapered bearings can be fabricated by using a tapered steel plate, or by tapering the elastomer layers for small tapers. Those bearings meet needs for inclined mounting situation sometimes
.
Types based on with/without PTFE sliding element
Ø With PTFE as sliding element mutually compatible with a stainless steel plate to accommodate larger movement. The PTFE is bonded onto a conventional elastomeric bearing and will mate with a stainless steel plate which is normally welded on the surface of masonry steel plate. Normal movements can be taken within the elastomer while greater movements (bigger shear force, usually infrequently occurring) can be realized thanks to the friction at the PTFE/stainless steel interface through sliding;

PTFE is just bonded to outer face of bearing, according to EN1337-3, Type D
1,Upper sole plate; 2,Stainless steel plate; 3,PTFE; 4,Lower sole plate; 5,Dustproof apron;
6,Anchor bolts; 7,mortar bed; 8,preset steel plate (if any)

PTFE is recessed in the steel plate (flange plate), according to EN1337-3, Type E
ØWithout PTFE, which is a conventional elastomeric bearing;
Types based on with/without external steel plates (anchor design)
With external steel plates which are vulcanized-boned into the elastomeric bearing, the mechanical attachment of bearing to the super/sub structure by using bolt or dowel becomes practicable and reliable. This way is excellent to stay the bearing in place reducing risk of skid over many live load cycles and make the replacement job easy.
Those external plates, also called “Sole Plates” or “Load Plates” or “Ancillary Plates” or “Masonry Plates”, are commonly welded to the girder or anchored with bolts. If they are welded there must be a detailed plan to mitigate excessive heat impact to the elastomer. IEC Engineers will be at your need for consultancy details.
The external plates can be added on both the upper and lower bearing surface, or either upper or lower surface. The plates could be plane steel plates or checkered steel plates.

Square bearing with outer steel plates (vulcanized)
The outer vulcanized plates can be checkered plates upon request.
Types based on with/without steel restraints (anchors)
ØWithout steel restraints.
ØWith steel restraints, fixed in all horizontal directions or one horizontal direction (so shear in the perpendicular direction).

rubber bearing with one-direction restraint
(IEC supplied 56 sets of such elastomeric bearings by Japanese design for Ambogo Bridge, Bridge Replacement for Improved Rural Access Project, Oro Province,Papua New Guinea)
There are a number of different ways to set up the restraints according to design. In combination of steel restraints, the bearing can be designed to be fixed or guided ones.
Plain Bearing
Plain bearing pads are utilized when load, deflection, rotation and expansion requirements are minimal.
Rubber compound:
Natural rubber (NR) or Chloroprene rubber (CR) with following properties, for details pls contact IEC.
Quality control at IEC
Elastomeric Bearings produced by IEC are under CE certified according to EN1337-3. All the required tests have been fulfilled in the ITT(Initial Type Test) and the FPC (Factory Production Control) is regularly monitored according to the regulations by MPA Stuttgart, Germany, a privileged independent supervisory body in the sector.
The external quality control is guaranteed by the internal quality control, which complies with the regulations stipulated in the EN1337-3 standard. Moreover, IEC ignores no detail in the internal QC procedures.
Trained inspectors and a full set of testing equipment including compression shear tester, ozone resistance tester, ageing tester, etc. guarantee a consistent quality level for all the IEC elastomeric bearings.

Full set of testing facilities to ensure quality constancy of rubber material
 Dy
Dy
Danamic compression-shear test machine with 30000kN vertical load and a 15% horizontal load ensures a large pool of bearing sizes can be tested in-house at IEC’s lab.
Production
A 2-storey building incorporating 2 downstream lines of advanced batching&mixing systems for rubber compounding signifies the pursuit of consistence in quality for engineering rubber products at IEC.

Batching & mixing lines at IEC
The advanced facilities ensure the formulations for synthesizing rubber compound are uniform and automatic for each elastomer fabrication.

Vulcanizing processing at IEC
The reinforcement steel plates are worked and prepared for vulcanization with presupposed procedures of automation. This process guarantees the constant production and minimizes the difference between each single bearing.
IEC stocks the moulds more than enough to meet the most common sized bearings.

320+ different sized moulds at stock
Quotations
Offers are provided based on project-related situation only. There is no standard quotation. Volume and lead time both impact the costing.
If the dimensions have been chosen, quotations will be offered according to the given information.
If not, following information must be provided to quote:
- Vertical loads (max and min)
- Design displacement (with restraint or not)
- Rotation requirement
- Shape of bearing
- Contact surface (permissible contact pressure, steel or concrete)
- Max available size (especially height restriction)
Quotations are to be read in junction with design drawings submitted by IEC and internal quality control inspection and test cost is included in the quotation. However, if the test is required at 3rd party, such test cost shall be quoted separately and be borne on the customer’s account.
Installations, maintenance and replacement
Consult IEC for details