We use cookies to enhance your experience. Read our policy so you can understand the types of cookies we use, the information we collect using cookies and how that information is used.Privacy Policy
Close
Confirm choices
Spherical Bearings were invented in 1970S along the development of the design principles of Pot Bearings. Large-scale cable-stayed bridges require much higher rotations up to 0.05 rad, accordingly, the compatible bridge bearings must also cater for this rotation. Apparently, Pot Bearings are not capable of such high rotation requirements.
Details
Spherical Bearing
Using history
Spherical Bearings were invented in 1970S along the development of the design principles of Pot Bearings. Large-scale cable-stayed bridges require much higher rotations up to 0.05 rad, accordingly, the compatible bridge bearings must also cater for this rotation. Apparently, Pot Bearings are not capable of such high rotation requirements.
By replacing the pot and elastomeric disc with a concave/convex contact mechanism, the rotation of Spherical Bearing can be largely enhanced. The actual application case has used 0.042 rad as rotational angle.
Vertical load can also be amplified by leaving out the elastomeric disc and using PTFE or higher compressive strength material. The largest ever know in China was produced by IEC, installed in Dashenguang Bridge over Yangtze River, Nanjing, taking vertical load of 140 MN.
Design principle
Spherical Bearings consist of a concave element, convex element and a top plate. PTFE mated to stainless steel plate slides against the spherical face, which provides rotational capacity and movement.
The essential part is the spherical cap. PTFE is ingeniously interlocked on the concave sphere and slides against the stainless steel plate which is typically weld-connected to the back of convex sphere. Rotation is realized through the sliding.
Another piece of PTFE is fixed on the top flat surface of the convex sphere, mated to the stainless steel plate to provide movement capacity.
PTFE is one type of sliding material and nowadays a higher level material, Ultra High Molecular Weight PE (UHMWPE) is popular due to its double compressive resistance capacity.

An exploded view of spherical bearing (guided type)

A convex sphere for spherical bearing during fabrication
Applied standards
l European Standard: EN 1337-7;
l British Standard: BS 5400-9.1, BS 5400-9.2;
l American Standard: AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specification and Construction specification
IEC was awarded CE certification for Spherical Bearings as per EN standard by KIT MPA Germany and the certificate of Performance of Constancy was cycled till date. We can also design and fabricate as per other standards and specifications.
Advantages of using Spherical Bearings
Ø Can adapt to high rotational capacity (up to 0.05 rad).
Ø Due to the identical design of rotation, more suitable for curved bridges.
Ø Eliminating the ageing or hardening issue of rubber, more suitable for extreme temperature situation such as frigid area.
Types
Same with Pot Bearing, Spherical Bearings can be fixed, guided sliding or free sliding.

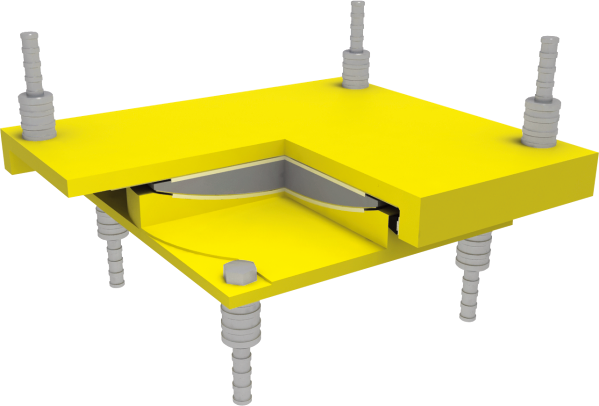
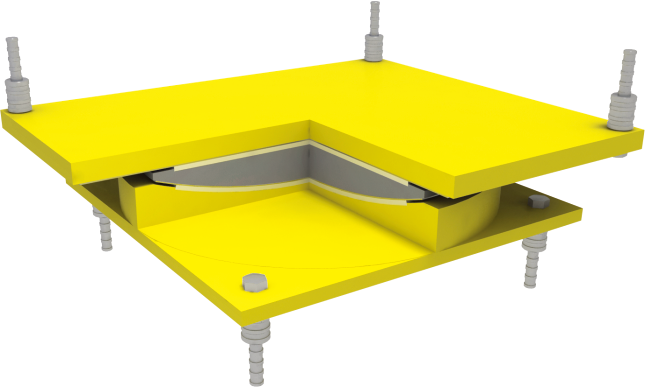
3d view of a fixed, guided sliding, free-sliding spherical bearing (typical design)
Materials
consult IEC for details
Steel element
Ø All steel elements except masonry plates are as per S355.
Ø Sometimes due to size concern, the concave sphere can also made of cast steel.
Ø Masonry plates are as per S235, unless otherwise noted.
Ø Stainless steel is as per S304.
Sliding material
Ø PTFE was largely used in the past but nowadays a much higher compressive strength material, Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), becomes popular and massively used.
Ø It was verified by China Railway Testing Laboratory (CRCC), confirming its compressive strength at different states and the wear loss at up to 50 kms distance (less than 5 microns per km)
Ø Due to the improved strength (at ULS 180 Mpa), the design of the bearing can be downsized and thus cost can be saved.

UHMWPE used in spherical bearing
Quality control and production
Refer to pot bearing
Installation, maintenance and replacement
Consult IEC for details.