We use cookies to enhance your experience. Read our policy so you can understand the types of cookies we use, the information we collect using cookies and how that information is used.Privacy Policy
Close
Confirm choices
IEC strip seal expansion joint, is a mechanically sealed joint with an extruded elastomeric seal retained by various options of profiled steel extrusions, often named as edgebeams or steel rails. The elastomeric seal, often referred to as strip seal, is mechanically locked into the cavity of steel extrusions to prevent the ingress of water or debris. At the side of steel extrusions, anchorage is affixed to be attached to the structure elements by a typical method of pouring high-strength concrete mortar, or other elastomeric mortar.
Details
IEC Stripseal Expansion Joint
1. Description
IEC strip seal expansion joint, is a mechanically sealed joint with an extruded elastomeric seal retained by various options of profiled steel extrusions, often named as edgebeams or steel rails. The elastomeric seal, often referred to as strip seal, is mechanically locked into the cavity of steel extrusions to prevent the ingress of water or debris. At the side of steel extrusions, anchorage is affixed to be attached to the structure elements by a typical method of pouring high-strength concrete mortar, or other elastomeric mortar.
This armored joint system is designed to cater for small movement ranging from 0mm to 120mm, while movements and rotations in all three axes are possible without any restraints.


example of a 3-D view of typical type of stripseal expansion joint
2. Material specifications
2.1 Edgebeam
Edgebeam is manufactured using hot-rolled/machined or hot-rolled/non-machined technology. Edgebeams are of grade of ASTM A709 Grade 50 or S355 or other equivalence or higher grade.


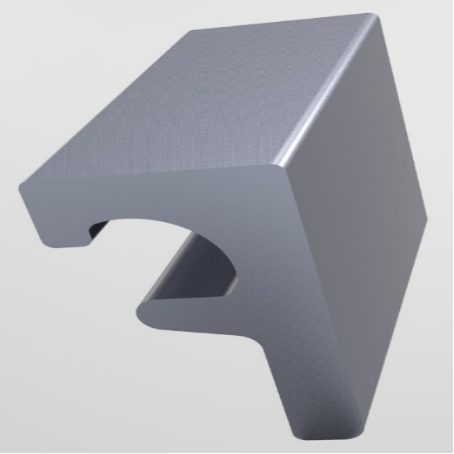
Type Z Type C Type F

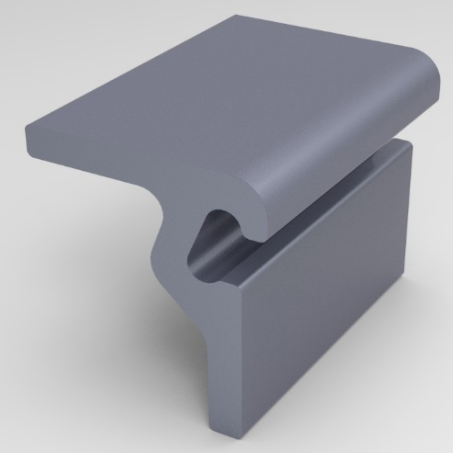
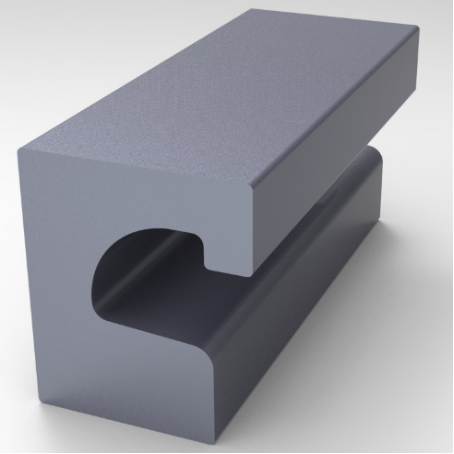
Type RG Type M Type C4
Various options of Edgebeams in 3D view
2.2 Rubber seal
The rubber seal can effectively get inserted into the cavity of the edgebeams without any screwed or bolted connections. Seals are watertight and extrude debris when closing. Moreover, it can be conveniently replaced from the road surface with simple tools.
Elastomeric seal is manufactured using extrusion technology and vulcanizing, and conform to ASTM D5973-97(2012) “standard specification for elastomeric stripseals with steel locking edge rails used in expansion joint sealing”.
Generally, IEC provides elastomeric seals made of EPDM. Neoprene seals are available upon request but rather than not recommended due to cost concern.
The working movement range for strip seal is typically 80mm, and can add up to 120mm with special design.
The strip seal can accommodate temperature from -40℃ to 60℃, and resistant high strength, oil, ozone, aging and salt water.
A approved type of lubricant-adhesive is necessary to be used during insertion of seal to ensure more reliable connection between edgebeam cavity and seal.



Type A seal (for type E, F, C4 and RG) Type B seal (for type C2 or M) Type C seal (for type M)
Properties of elastomeric seal
Properties | ASTM specification* | required value |
Hardness (Shore A Durometer) | ASTM D2240-04 | 70±5 |
Tensile Strength, Min. (MPa) | ASTM D412 | 15 |
Elongation at break, Min. (%) | ASTM D412 | 400 |
Heat Resistance (aged 70 h@100℃) | ||
Max. change in hardness | ASTM D573 | 10 |
Max. change in tensile strength (%) | ASTM D573 | -15 |
Max. Change in elongation (%) | ASTM D573 | -20 |
Compression set (aged 22 h@100℃) (%) | ASTM D395 | 20 |
Ozone resistance (100pphm, 20% strain at 37.7±1℃ 100 h) | ASTM D1149 | no crack |
Brittleness -40℃ | ASTM D746 | no failure |
Oil Swell 70 h@100℃ Max. Volume change (%) | ASTM D471 | -5 ~ +10 |
*other testing standards are also available and equivalent.
2.3 Anchorage
The edgebeams are rigidly connected to the main structure by anchors directly welded to the edgebeams. The traffic loads transferred from edgebeam to anchorages then to substructure. The anchorages are embedded in high strength mortar to assure the maximum resistance of traffic load.
Typically, anchorage is anchor stud, anchor plate, anchor loop or the combinations of them, all of which are ASTM A709 Grade 36 unless otherwise noted. The combination of anchor plate and anchor loop is used for very high traffic volumes.
Below are some examples of different edgebeams attached to different design of anchorages.
The other anchorage methods are also available upon customer design or specific request.


Z edgebeam + loop anchors (standard) E edgebeam + anchor loop and plate (shallow)
Selection of different anchorages mainly depends on the design traffic load and limitations of block-out dimensions.
If there is a skew (angleα) between the centerline of carriageway and the centerline of the joint, the anchors shall be arranged after calculations along the skew angle.
3. Working life and Warranty
The working life of IEC strip seal expansion joint shall be 50 years for unreplaceable components, i.e., edgebeam and anchorage, and 15 years for replaceable components, i.e., elastomeric seal.
IEC furnishes its customer with a 10 year warranty of strip seal expansion joint when the joint is properly installed and under regular maintenance. Force majeure such as seismic events or over-rolling will be precluded to this warranty.
4. Required data to fabricate a IEC strip seal expansion joint

L1 Length of upturn (without footway).
L2 Net width of bridge deck.
L3 Width of footway if any.
h2 Height from carriageway surface to footway surface (with footway).
α Skew angle if any.
β Upturn angle (when not specified, taken at 45°)
Consider the slope in transverse direction if any.
5. Type EMR strip seal expansion joint, a special type single-gap joint
EMR, an acronym for “Elastomeric Metal Runners”, consists of a rubber seal inserted between two metal runners while the anchorage uses the 2 sinusoidal bars. It is a unique system because the installation uses a rapid curing elastomeric resin which is bonded with bridge deck. No welding is needed thus the welding fatigue is eliminated.
What’s the most appealing feature of EMR is its short curing time of resin, which is typically 2~3 hours under 20℃ as installation temperature.
EMR can meet movement range up to 100mm. it is ideally suited for replacing the failure joint since the following superior performance:
wReliable connection. The rigid adhesive between elastomeric resin and bridge deck, can resist the traffic load and avoid the fatigue of welding.
wMinimum traffic disruption. Benefit from no welding and rapid curing elastomeric resin, the joint can allow traffic flow within 2-3 hours.
EMR resin specifications
Properties | ASTM test code | Required |
Compressive stress | D695 | min. 15.16MPa |
Rebound@5%deflection | D695 | min. 90% |
Impact resistance 0 ℃ -29 ℃ 70℃ | D5628 |
no cracking no cracking no cracking |
Shear strength | min. 1.72MPa |
Consult IEC for approved resin choices
Design detail

Model | Movement capacity | Recess size | Min. gap | Max. gap | |
C | D | Bmin | Bmax | ||
EMR-35 | 35 | 100 | 60 | 15 | 50 |
EMR-50 | 50 | 120 | 60 | 15 | 65 |
EMR-80 | 80 | 140 | 70 | 15 | 95 |
EMR-100 | 100 | 160 | 70 | 15 | 115 |


IEC is the first enterprise in China to introduce and utilize EMR joint technology for various projects in China and Southeast Asia. IEC has been supplying EMR joints rails for 20+ years.
6. Quality Control
✔Strict and regular quality control of the components and the assembly guarantees the good quality of the IEC strip seal expansion joints. In addition to our sub suppliers’ quality control, the checks are continued in our factory by means of tests on random samples.
✔Check on mill certificate and material identification
QC engineer and the fabrication supervisor will identify the material in the factory according to the Mill Certificate and Heat number (edgebeam, steel plate, steel stud or round steel).
✔Dimension check on edgebeam
Fabrication supervisor shall check dimensions and sections of the edgebeam.
QC engineer shall witness a minimum 10% of the above dimensional test randomly during the process.
Any disqualification once identified by QC engineer will be presented to QC manager and the unqualified material will be rejected or replaced to check.
✔Check on fabrication
Fabrication supervisor shall check the location and quantity of the anchorages for all edgebeams, and check the welding connection between edgebeams and anchorages.
QC engineer shall witness a minimum 10% of the above tests randomly during the process.
Any disqualifications identified by QC engineer shall be presented to QC manager and replaced before proceeding to the next work process.
✔Check on corrosion protection
Fabrication supervisor shall check a minimum 10% for dry film thickness of joint.
QC engineer shall witness all the above tests.
Any disqualifications identified by QC engineer shall be presented to QC manager and replaced before proceeding to the next work process.
✔Final inspection of joint
Fabrication supervisor shall conduct dimensional check and visual appearance checks on all the finished joints during the final assembly.
Quality control engineer shall witness a minimum 10% of the above tests.
Any disqualifications identified by QC engineer, shall be touched up to maintain the same effect.
✔Check on packaging
IEC QC engineer shall inspect the packaging of the joints according to the packing list for quantity and quality of the packages.