TWINSA
Case Study
Discovery 2: Transverse imbalance
By analyzing the load data, we easily identified asymmetric support conditions in some piers.
ZX01 Bearings:
Symmetric load distribution.
Left and right bearings carry similar loads.
ZX02 Bearings:
Significant asymmetry in load distribution.
The left bearing carries 57% more load than the right.
ZX03 Bearings:
The left bearings carry approximately 20% more load than the right.
ZX04 Bearings:
Symmetric load distribution.
Cause
Potential causes for the issue include shrinkage, creep, local settlement of the pier columns, or construction errors, which have resulted in the left bearings on ZX02 and ZX03 being slightly taller (by a few millimeters) than those on the right. These deviations are difficult to detect accurately using standard SHM methods.
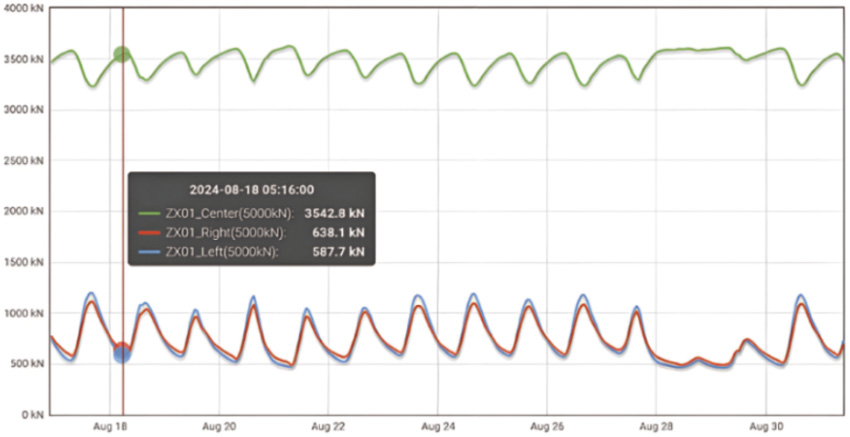
On ZX01, despite the center bearing load much higher than sides, the left and right bearings' load condition is highly symmetric.

On ZX02, Left bearing carries 57% more load than the right.
TWINSA Insights
The imbalance reduces overturning resistance on the right side, increasing the risk of overturning towards the left, especially when heavy trucks travel on the left side of the bridge deck.TWINSA recalculated the structural safety factor and found a reduction, indicating the need for a corrective construction plan to address the issue.Without TWINSA, this kind of problem could not be detected and quantified. To mitigate the issue, synchronous lifting would be required, necessitating the closure of traffic, which is both costly and resource-intensive. Furthermore, the effectiveness of such measures cannot be fully validated without reliable load monitoring.